Call it a gut instinct, but it seems like a lot of folks are resolving to cut the cable TV cord this year.
The people I’m increasingly talking to aren’t young techies, but longtime cable and satellite TV subscribers who’ve been pushed out by price hike after price hike. Especially for folks with fixed incomes, cord-cutting has become a necessity rather than a hobby.
This story is part of TechHive’s in-depth coverage of the best streaming devices.
But like so many other elements of technology, the field of cord-cutting is full of inscrutable acronyms, similar-sounding terminology, and nonsensical brand names. After covering this space for nearly a decade, it occurs to me that I’ve never bothered to define all of this jargon in one place.
Let’s rectify that oversight, then, with a glossary of terms that every current or future cord-cutter ought to know:
Basic cord-cutting terminology
Jared Newman / Foundry
Cord-cutting: The act of cancelling cable or satellite TV in favor of streaming and over-the-air TV options.
Streaming: In the context of television, the act of playing video from internet sources, or possibly from a local media server.
Streaming service: A provider of streaming video, usually delivered via an app or website. Examples include Netflix, Hulu, YouTube TV, and Sling TV. Also known as OTT (Over-the-Top) video.
Streaming device: A product that plugs into a television, enabling access to streaming services. Also known as a streaming player.
Smart TV: A television that can access streaming services without a separate streaming device.
Connected TV: A term that refers collectively to both streaming devices and smart TVs.
Streaming platform: Refers broadly to the software that runs on streaming devices and smart TVs. Examples include Roku, Fire TV, Android TV, and Google TV.
Streaming dongle: A small streaming device that plugs directly into the television without additional HDMI cables, and uses either the TV’s USB port or an AC outlet for power. Examples include the Roku Streaming Stick 4K, Amazon Fire TV Stick, and Chromecast with Google TV.
Streaming box: A streaming device that plugs into the television with an HDMI cable (because it’s too large to hang from that port, like a dongle does). A streaming box typically offers more features and processing power than a streaming dongle. Examples include the Apple TV 4K, Roku Ultra, and Amazon Fire TV Cube.
OTA: Short for Over-the-Air, this term refers to local TV channels received from an indoor or rooftop antenna. Here is a link to TechHive’s top TV antenna recommendations.
Types of streaming services
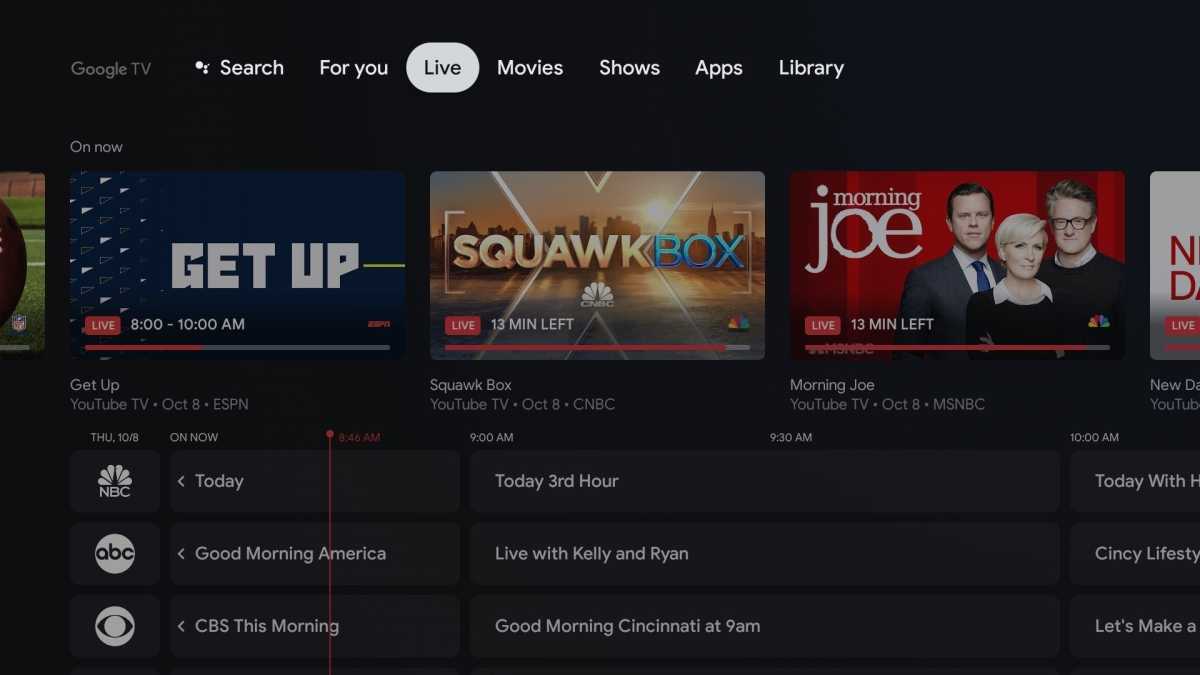
Jared Newman / IDG
SVOD: Short for “Subscription Video On Demand,” referring to services that primarily ask you to choose which movie or show to watch. Examples include Netflix, HBO Max, Amazon Prime Video, and Disney+.
FAST: Industry jargon for Free, Ad-Supported Television. Examples include Pluto TV, Tubi, and The Roku Channel. Also known as AVOD, short for Advertising-supported Video On Demand.
VOD: May refer generally to on-demand video, or specifically to rentals and purchases, as found on storefronts such as iTunes, Amazon Video, and Vudu. The latter may also be known as TVOD (Transactional Video On Demand), PVOD (Premium Video On Demand), or simply a la carte.
Linear TV: Video that plays on a pre-defined schedule, similar to cable. This format is especially popular with FAST services.
MVPD: Short for Multichannel Video Programming Distributor. This is industry jargon for cable, satellite, or telco TV services.
vMVPD: Short for virtual Multichannel Video Programming Distributor, the term refers to streaming services that offer a bundle of cable channels. Examples include YouTube TV, Hulu + Live TV, and DirecTV Stream. Synonyms include Live TV streaming service, and streaming TV bundles.
Skinny bundle: A live TV streaming service whose channel lineup is smaller—and therefore cheaper—than a typical cable package. Examples include Sling TV, Philo, and Frndly TV.
Streaming marketplace: A seller of subscriptions to multiple streaming services, usually with its own interface. Examples include Amazon Prime Video Channels, Roku Premium Subscriptions, and YouTube Primetime Channels.
IPTV: Technically describes a TV service delivered via internet protocol, but may also be used as shorthand for pirated streaming video sources.
Home networking jargon

Eero Pro 6 mesh Wi-Fi router
and satellite.
Jim Martin / Foundry
Internet modem or gateway: A device that delivers internet service into the home. Not to be confused with a Wi-Fi router, though some modems have routers built in. May also be known as an internet gateway or—for fiber internet providers—an ONT (short for Optical Network Terminal).
Router: A device that distributes internet connectivity from a modem or gateway to other network devices (clients) inside the home. A Wi-Fi router gives you the choice of using wired or wireless connections, assuming the client has a Wi-Fi adapter.
Ethernet: A standard for connecting smart devices–computers, smartphones, streaming boxes, storage devices, and other client devices–to form a local network with a router at its center. Ethernet networks can be wired or wireless.
Media server: A device that stores media files—including video and audio—and uses server software to stream those files to compatible devices on home network. The hardware used for media serving is most typically a NAS (network-attached storage) box. Examples of media server software include Plex, JellyFin, and Channels DVR.
Networked tuner: A device that streams over-the-air broadcasts to other devices on the same network. Examples include HDHomeRun, Tablo, and AirTV.
TV terminology

Jared Newman / Foundry
4K: Refers to video content with resolution of 3840 x 2160 pixels, or to devices capable of playing such content. Also known as Ultra HD.
HDR: Short for High Dynamic Range, the term refers to video with a wider contrast range than standard content, allowing for more detailed highlights and shadows on televisions that support HDR.
Dolby Vision: A proprietary version of HDR that can map colors on a scene-by-scene basis, resulting in better accuracy when viewed on televisions that support Dolby Vision.
HDR10+: A royalty-free equivalent to Dolby Vision, most notably supported by Amazon Prime.
Dolby Atmos: An object-based audio format that adds the dimension of height to surround sound on compatible soundbars or A/V systems and loudspeakers.
FPS: Short for Frames Per Second, which measures how smooth motion in video appears to the human eye (the higher the better). A frame rate of 30 frames per second is typical, but a frame rate of 60 FPS is especially important for sports programming, so it’s worth paying attention to this spec when evaluating live TV streaming services.
Did I miss anything? Let me know, and I’ll add it to the glossary. And for more advice on how to finally ditch cable, sign up for my Cord Cutter Weekly newsletter.

