The mobile games industry can be defined by two core qualities: it is data-driven and it moves incredibly quickly. Decisions made without a deeper understanding of the driving influences of the sector can and will be costly.
With over 15 years of experience analysing the games industry, Piers Harding-Rolls, Ampere Analysis research director and head of the games research team, breaks down the biggest trends in the mobile and broader games industry in his monthly column, Insight.
Our latest outlook forecasts that the world games content and services market will decline in 2022 to $188 billion (-1.2 per cent). Following a strong market performance in 2021 (up five per cent, $191 billion), the sector landscape has become increasingly unsettled during the first six months of 2022.
While the global pandemic has raged, the games market has expanded hugely, adding 26 per cent to its scale and $39 billion in spending from 2019 to 2021. Now that many countries have returned to more normality, it is inevitable that consumer attention on gaming will in some cases become more diluted, especially in mature markets.
Ampere’s consumer research from Q2 2022 has shown a drop in share of the population that self-report as active gamers in a number of the most established markets – Japan, South Korea, US and UK – compared to Q2 2021.
Russia was the 10th biggest games market in 2021
Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and the subsequent market fallout will unsurprisingly drag down games spending in those markets. Ampere is forecasting the Russian market to drop to number 14 in the global ranking in 2022 and for it to lose $1.2 billion in value compared to the previous year.
There is continued uncertainty about when, or even if, the market will return to its previous performance. With many major games companies halting their business in response to the invasion, restarting these in the near-term is unlikely to happen.
Games sales are not immune to macroeconomic turbulence
As we progress through a period of heavy inflation, with an increasing cost-of-living squeeze and a higher potential for a recession, it is inevitable that the games market will be negatively impacted in certain areas. The idea that the games market is entirely ‘recession proof’ is a fallacy.
Indeed, the fact that the games sector is now as broad as it is suggests that there are likely to be more cases where a cost-of-living squeeze will impact consumption compared to 2008 and 2009 when the last major global recession took hold. Games hardware and spending in live service games are areas we will be keeping an eye on.
However, games remain very good value for money and if consumers dial back on other discretionary spending but are at home more, the sector will be relatively well insulated from some of the worst effects of a global slowdown. Ampere currently expects the global market to spring back in 2023 as mature markets stabilise and growth markets continue the adoption of gaming.
Mobile gaming set for a decline of 1.3 per cent
Beyond the macroeconomic and post-pandemic attention factors, each device category is also experiencing other factors that are impacting performance. Ampere’s current year-on-year outlook forecasts the mobile gaming segment to decline by 1.3 per cent. PC gaming is also expected to decline, by three per cent. Console gaming performance is forecast to be flat, while the cloud segment – which includes pure streaming subscription services only – is expected to grow strongly from a very small base.
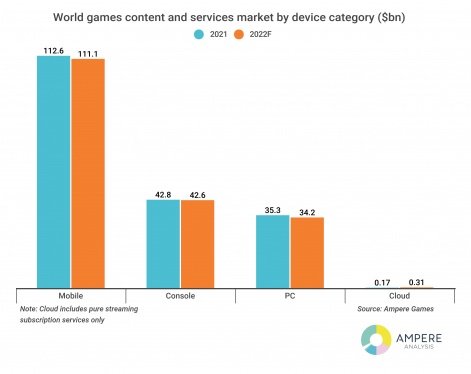
The biggest segment of the market, mobile gaming, continues be challenged by changes to platform privacy settings, which have turned on its head the ability to target specific cohorts and track advertising performance. This is disrupting user acquisition, and parts of the industry will need more time to effectively rebuild tactics to overcome these changes.
While the biggest mobile games companies have been able to use their substantial content networks and user acquisition teams to develop new tactics to help mitigate for these changes, there is a long tail of smaller games companies that don’t have the resources to develop new approaches in a systematic way. Just last month, PocketGamer.Biz covered an industry survey by Tenjin and Growth FullStack which reported that 68 per cent of respondents found mobile game marketing more difficult following ATT changes.
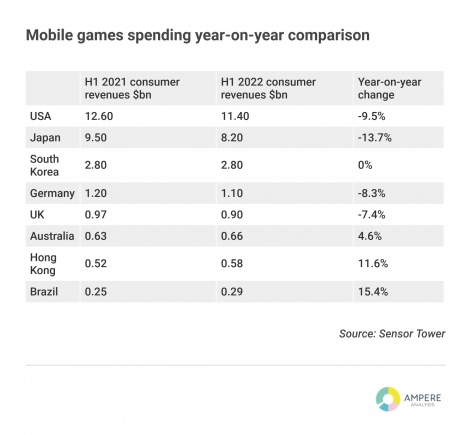
It is almost impossible to unpick the exact impact of each specific factor that has led to mobile games spending across a combined Apple App Store and Google Play to decline in the first six months of 2022, according to Sensor Tower. It is also true that for some gamers it will be a combination of factors that tip them into reducing their spend – for example, the compound impact of less attention on gaming and a squeeze on entertainment spending, adding further complexity to the landscape.
Sensor Tower data reveals that well-established mobile games markets have suffered in the first half of the year, with the US seeing a 9.5 per cent year-on-year drop in consumer revenues, Japan a 13.7 per cent drop, the UK down 7.4 per cent and Germany declining 8.3 per cent.
South Korea has had flat performance, while Hong Kong has grown significantly by 11.6 per cent, coinciding with a heavy wave of covid infections in the first half of the year. Other less-established markets, such as Brazil, continue to grow strongly from a smaller base (up 15.4 per cent).
Supply chain and production challenges are negatively impacting console gaming
The second biggest segment, console gaming, is being negatively impacted by the continued limited availability of console hardware and the delays to numerous triple-A titles, many of which have slipped into 2023.
PC gaming was disrupted during the pandemic in key Asian markets due to the shutdown of internet cafes. It has since bounced back but still faces the underlying threat of cannibalization from mobile gaming, with many PC-game franchises being released as mobile apps. At the premium end of the market, delays to triple-A releases will also have a negative impact.
Lastly, cloud subscription services – as a standalone proposition – remain very nascent although growing fast due to the launch of a number of new services. Primarily, streaming distribution is being used most effectively as a value-added proposition for established download subscription services such as Xbox Game Pass.

